Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION
CSS stands for CASCADING STYLE SHEETS. It is used to used to control the appearance and layout of web pages written in HTML. It allows you to apply styles such as colors, fonts, spacing, alignment, and positioning to elements, helping create visually appealing and user-friendly websites.
Like HTML, CSS is not a programming language. It is neither a markup language. It is a style sheet language. A style sheet language is a computer language used to describe the presentation (look and formatting) of a document written in a markup language like HTML or XML. Example: CSS, XSL (Extensible Stylesheet Language), DSSSL (Document Style Semantics and Specification Language).
If you are new to web-development it is advised to learn HTML first and then proceed to CSS beacuse CSS is written for HTML elements. You can Learn HTML at this LINK LEARN_HTML
STRUCTURE OF CSS
CSS is rule-based language. It works by selecting HTML element and writing a ruleset for that element. Ruleset is generally known as rule. Let us explore the various parts of ruleset in detail.
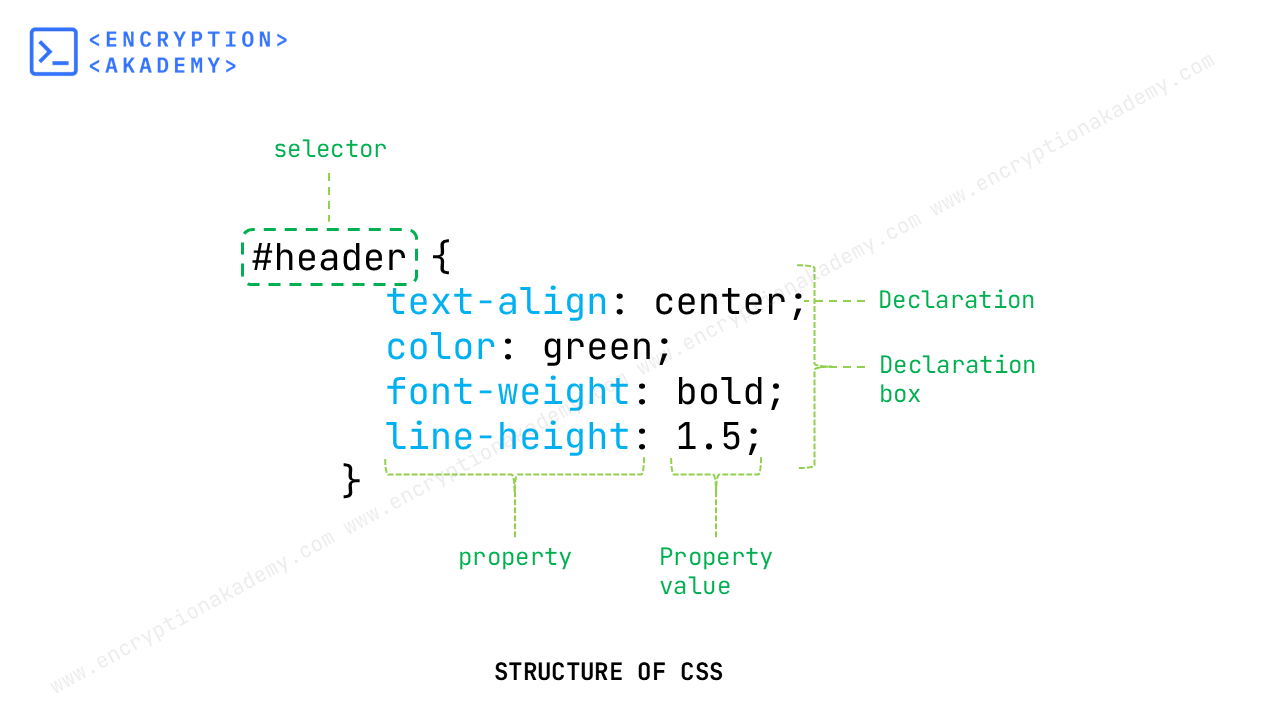
1. Selector
Selector is name of HTML element to which style is applied. Selectors are of various types like element selector, ID selector, Class selector, pseudo selector and others. We will learn about selectors in detail in our CSS_Selectors section.
2. Declaration
Declaration is a single rule in ruleset. When writing a rule, developer targets a property of element and define it. Declaration is written in Propery:value format.
3. Properties
Properties are the different characteristics of element which you can style. Each element has different set of properties. Some properties are common among elements. We will learn about properties in detail in upcoming CSS lessons.
4. Property Value
Property Value is written to right of property after the colon. It can be numerical or text value depending on the property.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is CSS class names case-sensitive?
Is HTML and CSS the same?
| Aspect | HTML | CSS |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Structures the content of a webpage | Styles the appearance of that content |
| Function | Creates elements like headings, paragraphs, images, links | Changes layout, colors, fonts, spacing, and design |
| Syntax | Uses tags like <p>, <h1>,
<img>
|
Uses selectors and properties like color,
margin
|
| Example | <p>Hello World</p> |
p { color: red; } |
| Dependency | Can exist alone | Needs HTML to apply styles to |
Can css and html be in same file?
Who Invented CSS?

Håkon-Wium-Lie
Why is CSS called "Cascading"?
| Order of Priority (High to Low) |
Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Inline styles | Styles written directly in the element tag |
| 2. Internal and external stylesheets | Based on specificity and source order |
| 3. Browser default styles | The browser’s built-in stylesheet |
| 4. User-defined styles | Styles defined by users in their browsers (rare) |
Will CSS change in the future?
- To support modern design trends
- To improve performance and responsiveness
- To make code cleaner and more powerful
- To reduce reliance on JavaScript for layout and animation
What does CSS stand for?
Cascading: Refers to how CSS applies multiple rules, resolving conflicts using priority (cascade).
Style: CSS controls the appearance (style) of web elements—like colors, fonts, spacing, and layout.
Sheets: Styles are stored in files or blocks called style sheets, which can be reused across web pages.
How do you convert CSS code into SCSS format?
| Online Tools | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| SassMeister | Online SCSS compiler and editor | sassmeister.com |
| CSS2SCSS | Convert CSS to SCSS automatically | css2scss.herokuapp.com |
| lambdatest | convert CSS files to SCSS format files with a click | codepen.io |
| JSFiddle | Online code editor for web snippets | jsfiddle.net |
Is there a tool to convert regular CSS into Tailwind CSS classes?
| Online Tools | Description | Link |
|---|---|---|
| Tailwind Play | Official Tailwind CSS playground | play.tailwindcss.com |
| css-to-tailwind | Converts CSS styles to Tailwind classes | transform.tools/css-to-tailwind |
| Tailwind Converter | Converts CSS snippets to Tailwind CSS | tailwind-converter.netlify.app |
| Windy | Tailwind CSS IntelliSense & conversion | windyapp.dev |
What is the difference between CSS and SCSS?
| Feature | CSS | SCSS (Sass) |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Cascading Style Sheets | Sassy CSS (Syntactically Awesome Stylesheets) |
| Syntax | Standard CSS syntax | Superset of CSS with added features (supports CSS syntax plus extra) |
| Variables | Not supported | Supported (e.g., $primary-color: #333;) |
| Nesting | Not supported | Supported (nest selectors inside others) |
| Mixins & Functions | Not supported | Supported (reusable blocks of styles) |
| Compilation | No compilation needed; directly interpreted by browsers | Needs to be compiled into CSS before use in browsers |
| Learning Curve | Easy to learn | Slightly steeper due to added features |
| Use Case | Simple styling, small projects | Large projects requiring maintainability and modularity |
What is the difference between CSS and HTML?
| Feature | HTML | CSS |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | HyperText Markup Language | Cascading Style Sheets |
| Purpose | Structure and content of a webpage | Styling and layout of webpage elements |
| Type | Markup language | Style sheet language |
| What it Defines | Elements like headings, paragraphs, links, images | Colors, fonts, spacing, positioning, animations |
| Browser Role | Interprets HTML to build the webpage structure | Interprets CSS to apply visual styles to HTML elements |
| File Extension | .html or .htm | .css |
| Syntax | Tags and attributes (e.g., <p>, <a href>) | Selectors and properties (e.g., p { color: red; }) |
| Can Work Without | CSS (but looks plain) | HTML (no styling without content) |
 Published: 19 Jun
2025
Published: 19 Jun
2025 3-min read
3-min read
